...
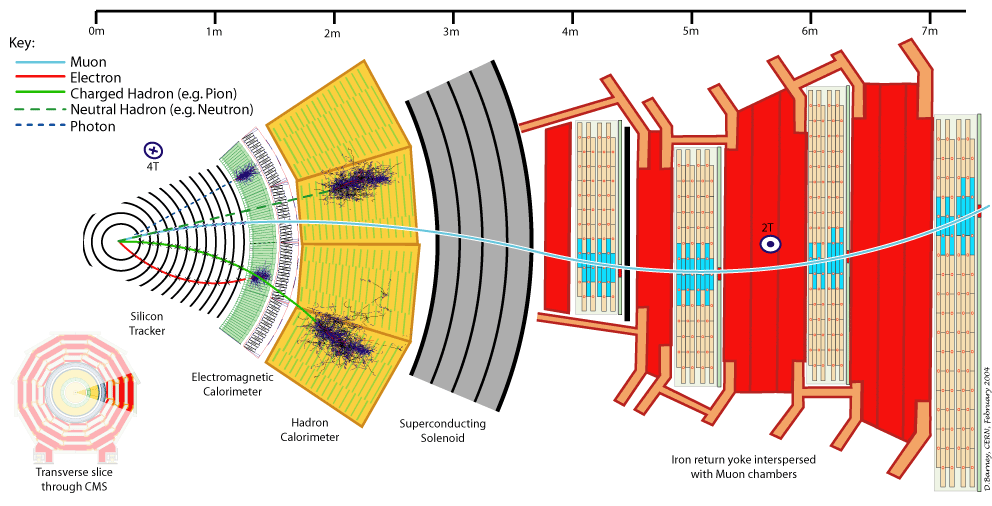
Let's first understand what are the experimental signatures and how the LHC's detectors work at the LHC experiment. As an example, this is a sketch of the Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) detector.
A collider detector is organized in layers: each layer is able to distinguish and measure different particles and their properties. For example, the silicon tracker detects each particle that is charged. The electromagnetic calorimeter detects photons and electrons. The hadronic calorimeter detects hadrons (such as protons and neutrons). The muon chambers detect muons (that have a long lifetime and travel through the inner layers).
...